Testing Behavior#
Testing Configuration#
By default, Cosmos will add a test after each model. This can be overridden using the test_behavior field in the RenderConfig object.
Note that this behavior is different from dbt’s default behavior, which runs all tests after all models have been run.
Cosmos defaults to running tests after each model to take a “fail-fast” approach to testing. This means that if a model
runs with failing tests, the rest of the project is stopped and the failure is reported. This is in contrast to dbt’s
default behavior, which runs all models and tests, and then reports all failures at the end.
Cosmos supports the following test behaviors:
after_each(default): turns each model into a task group with two steps: run the model, and run the testsbuild: (since Cosmos 1.8) run dbt resources using thedbt buildcommand, using a single task. This applies to dbt models, seeds and snapshots.after_all: each model becomes a single task, and the tests only run if all models are run successfullynone: don’t include tests
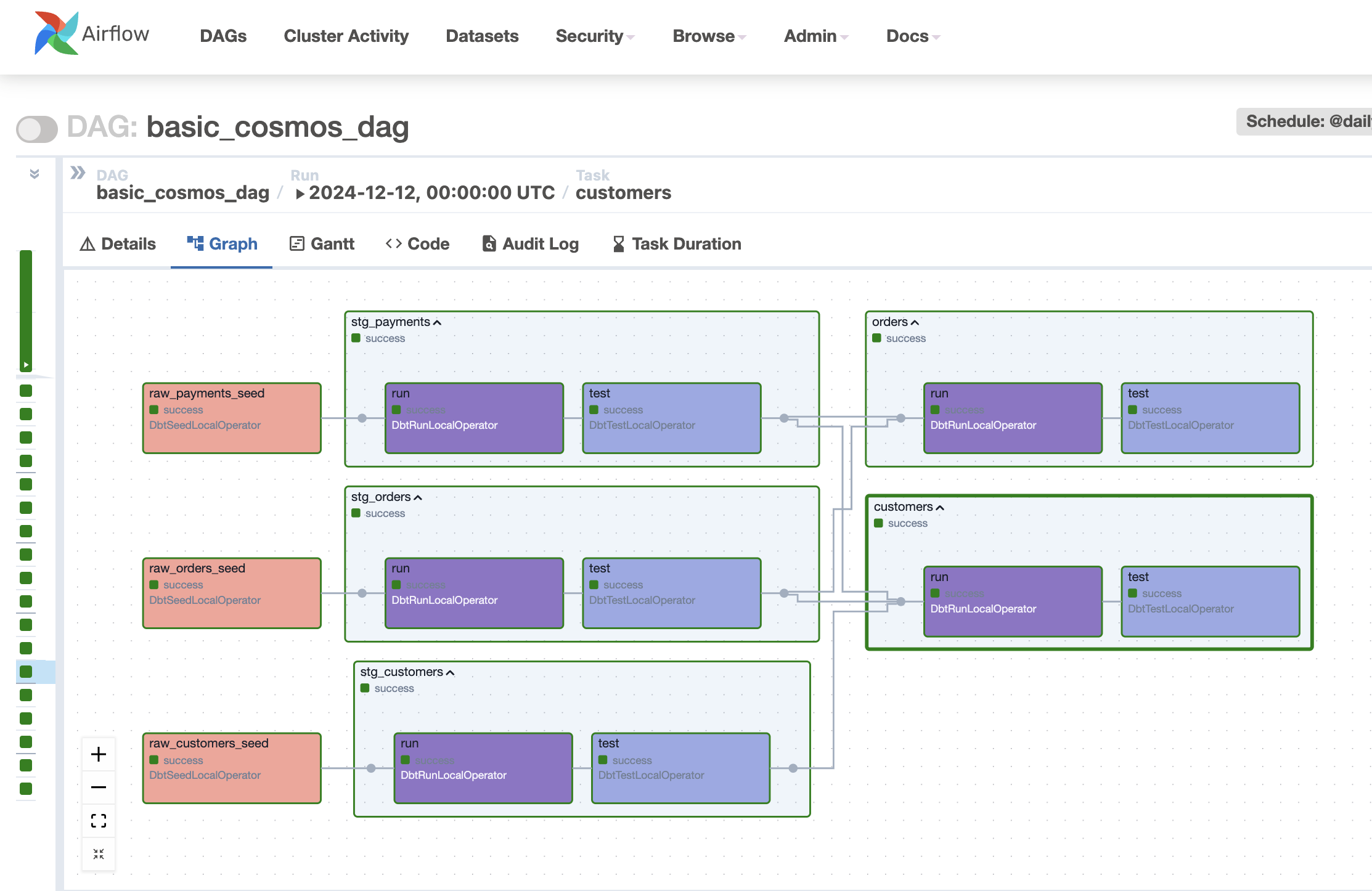
Example of the standard behavior of TestBehavior.AFTER_EACH,
when using the example DAG available in dev/dags/basic_cosmos_dag.py:
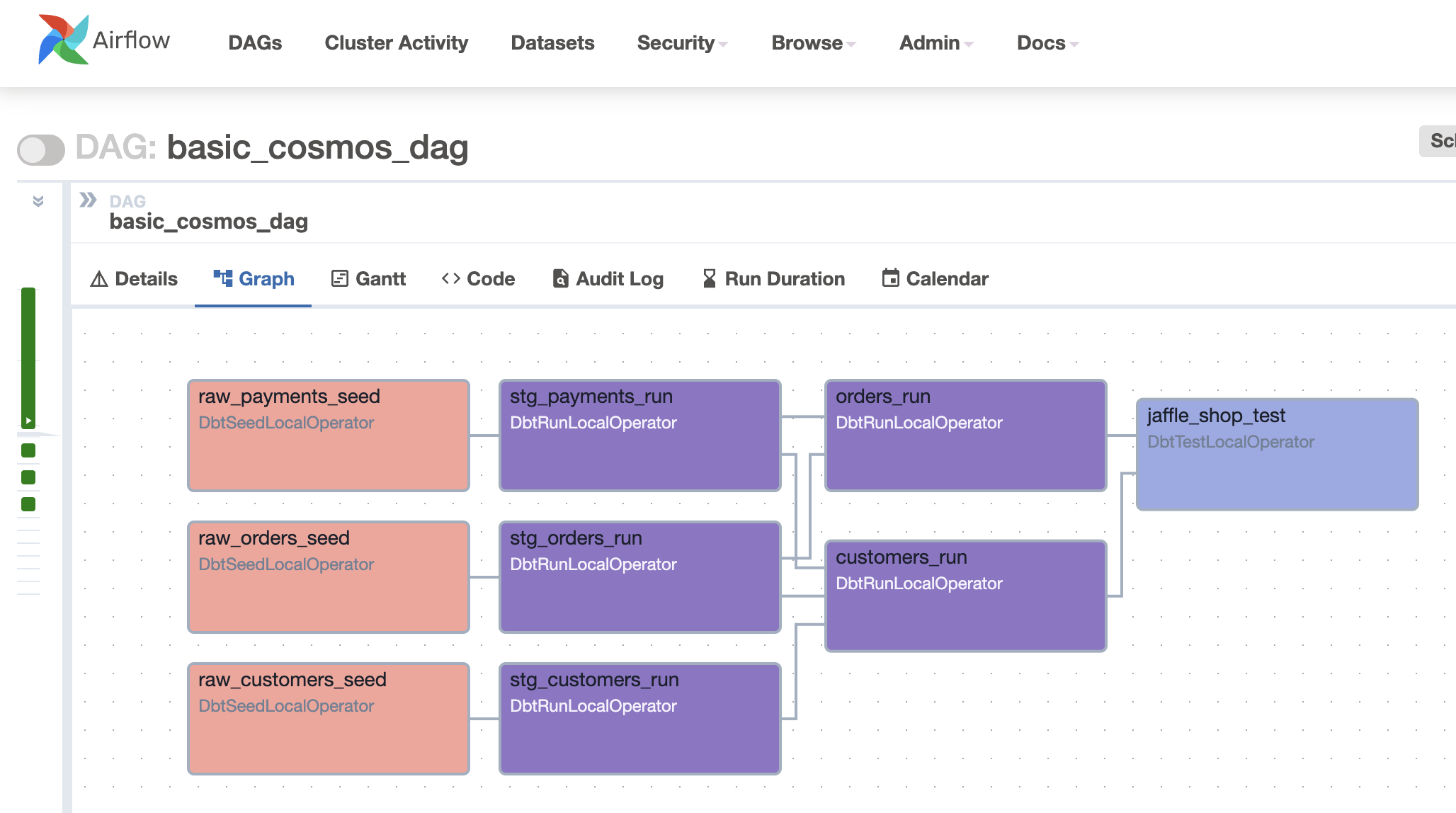
Example when changing the behavior to use TestBehavior.AFTER_ALL:
from cosmos import DbtTaskGroup, RenderConfig
from cosmos.constants import TestBehavior
jaffle_shop = DbtTaskGroup(
render_config=RenderConfig(
test_behavior=TestBehavior.AFTER_ALL,
)
)
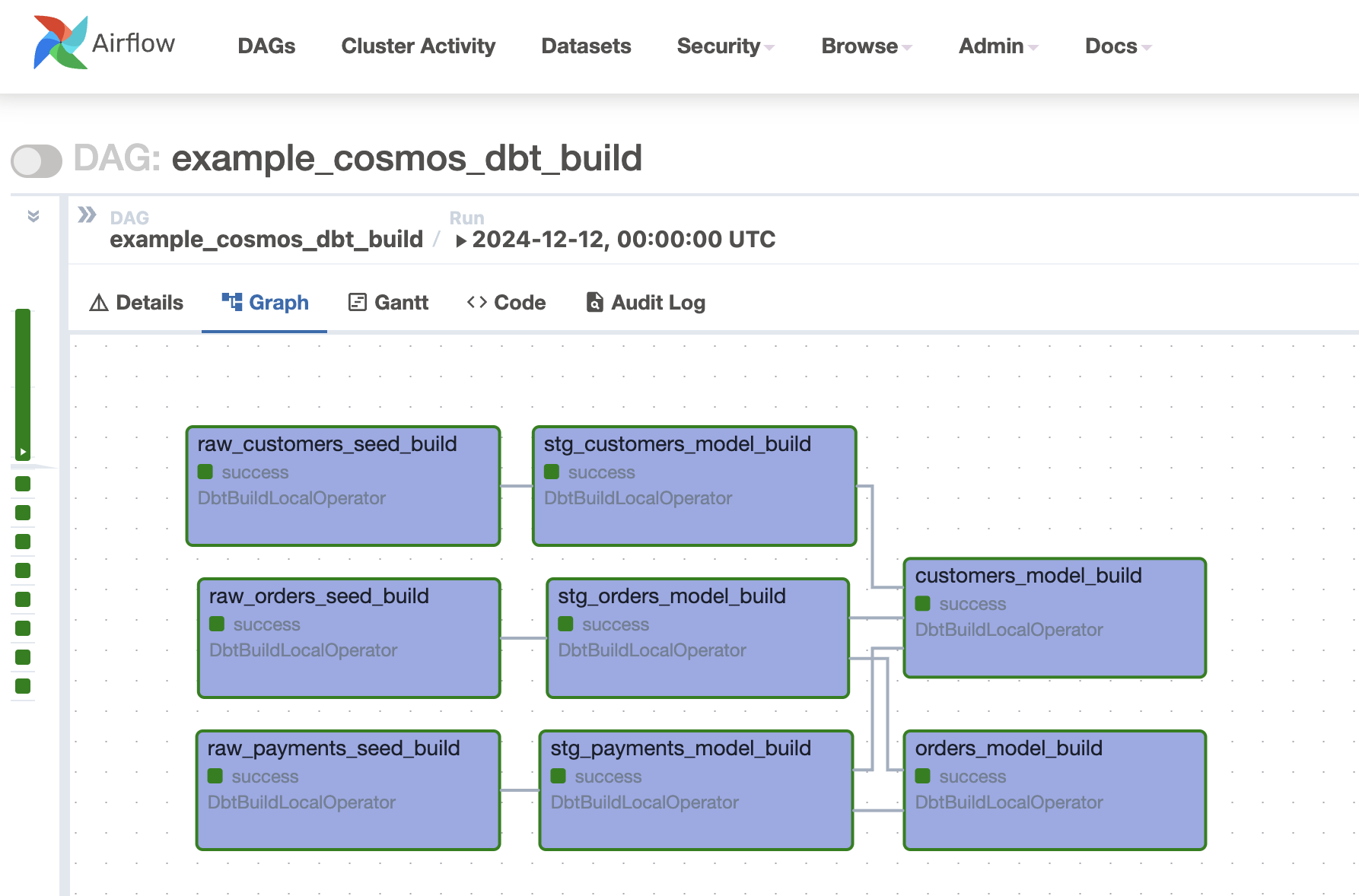
Finally, an example DAG and how it is rendered in the Airflow UI when using TestBehavior.BUILD (available since Cosmos 1.8):
example_cosmos_dbt_build = DbtDag(
# dbt/cosmos-specific parameters
project_config=ProjectConfig(
DBT_ROOT_PATH / "jaffle_shop",
),
render_config=RenderConfig(
test_behavior=TestBehavior.BUILD,
),
profile_config=profile_config,
operator_args={
"install_deps": True, # install any necessary dependencies before running any dbt command
"full_refresh": True, # used only in dbt commands that support this flag
},
# normal dag parameters
schedule="@daily",
start_date=datetime(2023, 1, 1),
catchup=False,
dag_id="example_cosmos_dbt_build",
default_args={"retries": 0},
)
Warning Behavior#
Note
As of now, this feature is only available for the default execution mode local, virtualenv and kubernetes
Cosmos enables you to receive warning notifications from tests and process them using a callback function.
The on_warning_callback parameter adds two extra context variables to the callback function: test_names and test_results.
test_names contains the names of the tests that generated a warning, while test_results holds the corresponding test results
at the same index. Both the test_names and test_results variables are lists of strings.
For example, the following code snippet shows how to send a Slack message when a warning occurs:
from cosmos import DbtDag
from airflow.providers.slack.hooks.slack_webhook import SlackWebhookHook
from airflow.utils.context import Context
def warning_callback_func(context: Context):
tests = context.get("test_names")
results = context.get("test_results")
warning_msgs = ""
for test, result in zip(tests, results):
warning_msg = f"""
*Test*: {test}
*Result*: {result}
"""
warning_msgs += warning_msg
if warning_msgs:
slack_msg = f"""
:large_yellow_circle: Airflow-DBT task with WARN.
*Task*: {context.get('task_instance').task_id}
*Dag*: {context.get('task_instance').dag_id}
*Execution Time*: {context.get('execution_date')}
*Log Url*: {context.get('task_instance').log_url}
{warning_msgs}
"""
slack_hook = SlackWebhookHook(slack_webhook_conn_id="slack_conn_id")
slack_hook.send(text=slack_msg)
mrr_playbook = DbtDag(
# ...
on_warning_callback=warning_callback_func,
)
When at least one WARN message is present, the function passed to on_warning_callback will be triggered. In the example above, the following message will be sent to Slack:

Note
If warnings that are not associated with tests occur (e.g. freshness warnings), they will still trigger the
on_warning_callback method above. However, these warnings will not be included in the test_names and
test_results context variables, which are specific to test-related warnings.
Tests with Multiple Parents#
It is common for dbt projects to define tests that rely on multiple upstream models, snapshots or seeds.
By default, Cosmos will attempt to run these tests using the behavior defined using test_behavior as previously explained.
As an example, if there is a test that depends on multiple models (model_a and combined_model), and the DAG uses
TestBehavior.AFTER_EACH, Cosmos will attempt to run this test twice after each model run.
While the standard behavior of Cosmos works for many cases, there are a few scenarios when the test fails unless both models
run. To overcome this issue, starting in Cosmos 1.8.2, we introduced the parameter
should_detach_multiple_parents_tests in RenderConfig. By default, it is False. If it is set to True and
TestBehavior is AFTER_EACH or BUILD, Cosmos will identify all the test nodes that depend on multiple parents
and will create a standalone test task for each of them.
Cosmos will attempt to name this task after the test’s original name. However, since some test names can exceed 250 characters and Airflow does not support IDs longer than this limit, Cosmos will assign names like “detached_0_test,” incrementing the number as needed.
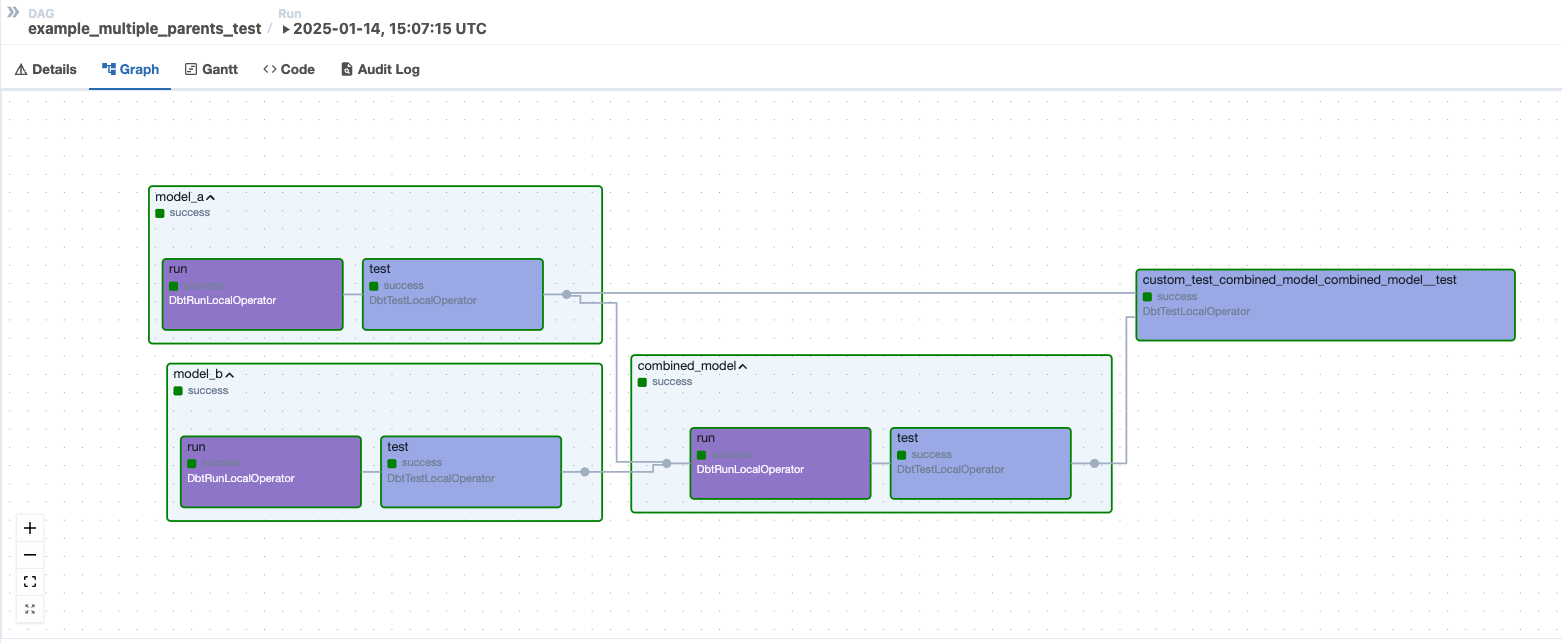
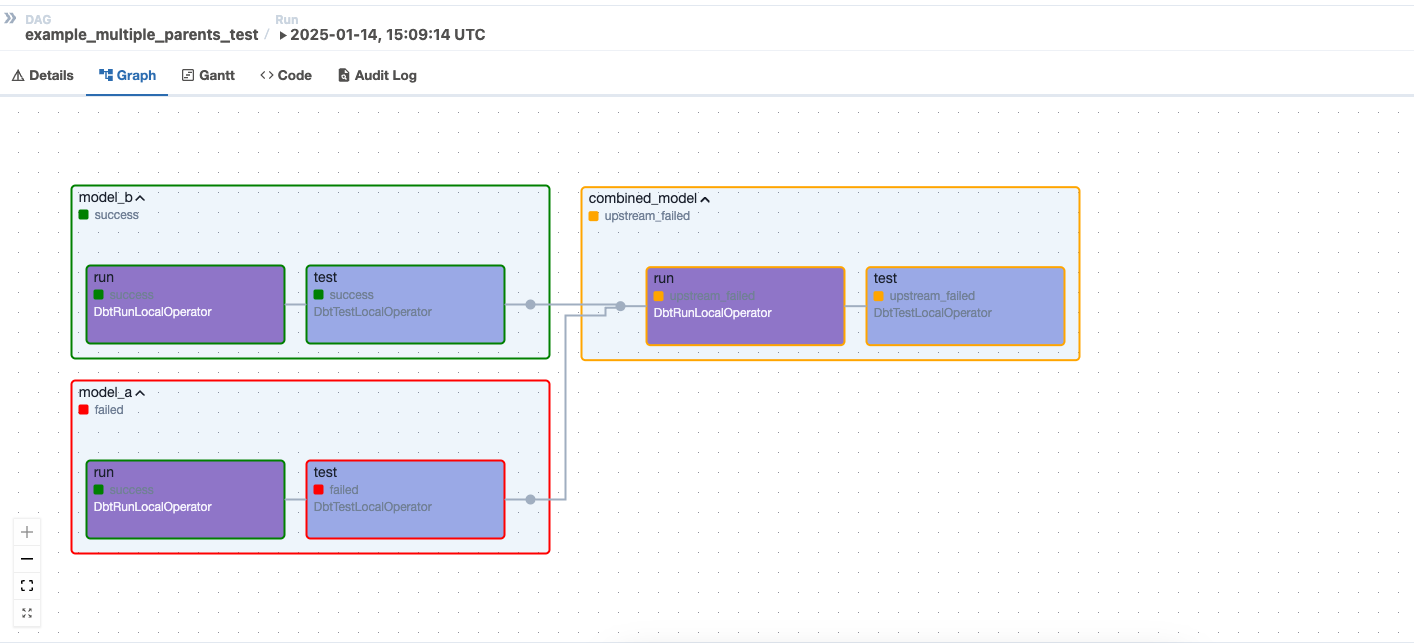
The DAG example_tests_multiple_parents illustrates this behavior. It renders a dbt project named multiple_parents_test that has a test called custom_test_combined_model that depends on two models:
combined_model
model_a
By default, Cosmos will error:
[2024-12-27T12:07:33.564+0000] {taskinstance.py:2905} ERROR - Task failed with exception
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/Users/tati/Code/cosmos-clean/astronomer-cosmos/venvpy39/lib/python3.9/site-packages/airflow/models/taskinstance.py", line 465, in _execute_task
result = _execute_callable(context=context, **execute_callable_kwargs)
File "/Users/tati/Code/cosmos-clean/astronomer-cosmos/venvpy39/lib/python3.9/site-packages/airflow/models/taskinstance.py", line 432, in _execute_callable
return execute_callable(context=context, **execute_callable_kwargs)
File "/Users/tati/Code/cosmos-clean/astronomer-cosmos/venvpy39/lib/python3.9/site-packages/airflow/models/baseoperator.py", line 401, in wrapper
return func(self, *args, **kwargs)
File "/Users/tati/Code/cosmos-clean/astronomer-cosmos/cosmos/operators/local.py", line 796, in execute
result = self.build_and_run_cmd(context=context, cmd_flags=self.add_cmd_flags())
File "/Users/tati/Code/cosmos-clean/astronomer-cosmos/cosmos/operators/local.py", line 654, in build_and_run_cmd
result = self.run_command(cmd=dbt_cmd, env=env, context=context)
File "/Users/tati/Code/cosmos-clean/astronomer-cosmos/cosmos/operators/local.py", line 509, in run_command
self.handle_exception(result)
File "/Users/tati/Code/cosmos-clean/astronomer-cosmos/cosmos/operators/local.py", line 237, in handle_exception_dbt_runner
raise AirflowException(f"dbt invocation completed with errors: {error_message}")
airflow.exceptions.AirflowException: dbt invocation completed with errors: custom_test_combined_model_combined_model_: Database Error in test custom_test_combined_model_combined_model_ (models/schema.yml)
relation "public.combined_model" does not exist
LINE 12: SELECT id FROM "postgres"."public"."combined_model"
^
compiled Code at target/run/my_dbt_project/models/schema.yml/custom_test_combined_model_combined_model_.sql
However, if users set should_detach_multiple_parents_tests=True, the test will be detached, as illustrated below.
The test will only run once after both models run, leading the DAG to succeed:
from cosmos import DbtDag, RenderConfig
example_multiple_parents_test = DbtDag(
...,
render_config=RenderConfig(
should_detach_multiple_parents_tests=True,
),
)